Why 2026 Classrooms Need More Creative Activities
Education systems around the world are changing rapidly, and classrooms in Singapore are no exception. As we move closer to 2026, educators and parents are recognising that traditional teaching methods alone are no longer enough to prepare students for the future. Academic knowledge remains important, but it must be complemented by creativity, adaptability, and emotional intelligence.
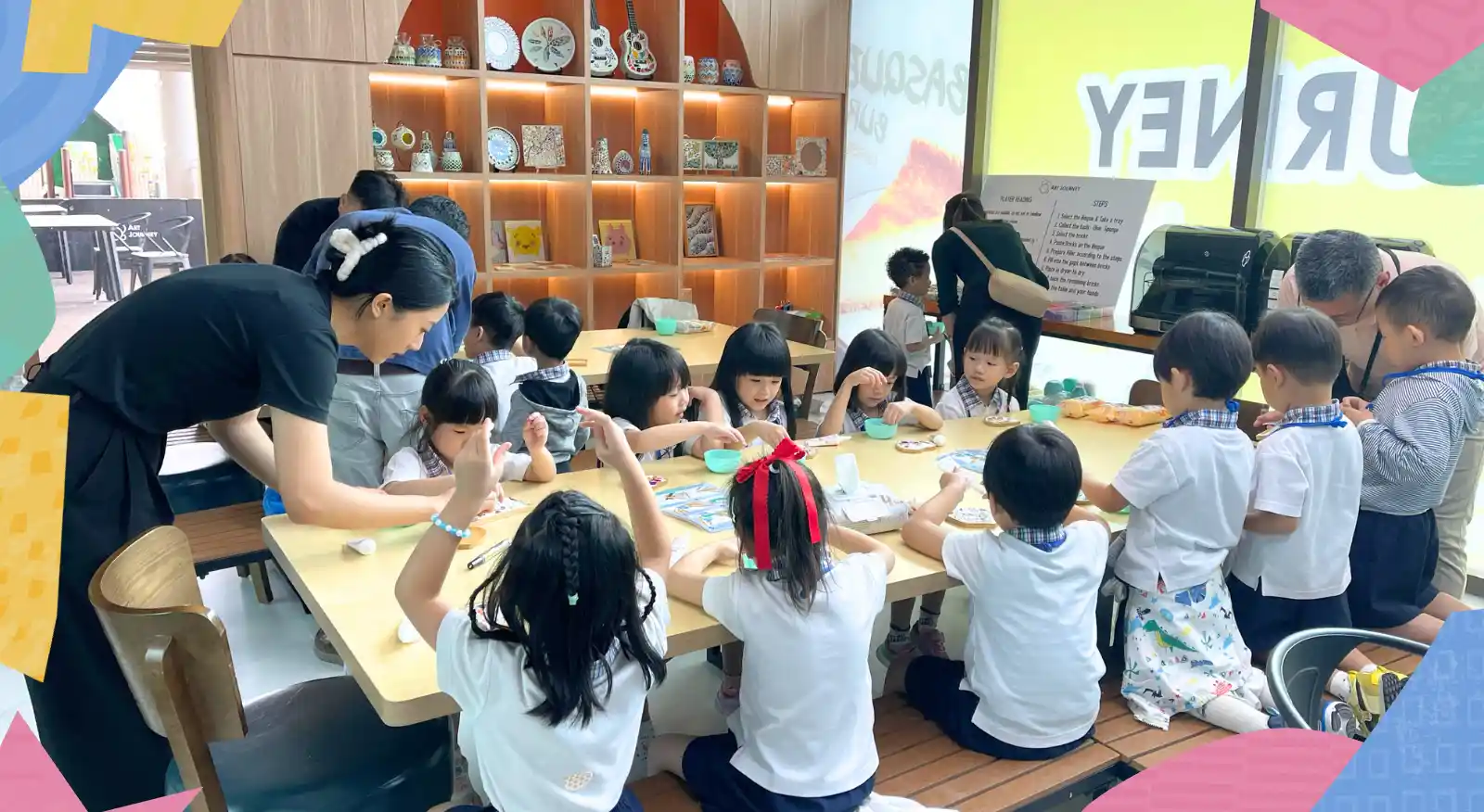
Creative activities—such as art, hands-on projects, and exploratory learning—are becoming essential components of effective education. They support not only academic understanding but also the personal and social development of students. In 2026, classrooms that embrace creativity will be better equipped to nurture confident, resilient, and future-ready learners.
The Changing Demands of Future Education
The future workforce will look very different from today’s. Automation, artificial intelligence, and digital tools are transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. While factual knowledge can be accessed instantly, skills like creativity, problem-solving, and original thinking remain uniquely human.
Classrooms must evolve to reflect this reality. Creative activities help students learn how to:
- Think independently
- Explore multiple solutions
- Adapt to new challenges
- Express ideas clearly and confidently
By integrating creativity into everyday learning, schools can prepare students for a future that values innovation over memorisation.
Creativity Supports Deeper Learning, Not Distraction
There is a common misconception that creative activities distract students from “real” learning. In reality, creativity enhances understanding. When students engage in creative tasks, they process information more deeply and retain knowledge longer.
For example, drawing concepts, building models, or expressing ideas through art allows students to:
- Visualise abstract ideas
- Connect theory with real-world application
- Learn through experience rather than repetition
Creative learning transforms passive absorption into active engagement.
Addressing Diverse Learning Styles in the Classroom
Not all students learn in the same way. Some excel through reading and writing, while others learn best through visual or hands-on experiences. A classroom that relies solely on textbooks and lectures may unintentionally leave many students behind.
Creative activities support:
- Visual learners through imagery and design
- Kinesthetic learners through hands-on creation
- Reflective learners through self-expression
By incorporating creativity, classrooms become more inclusive and supportive of different learning needs.
Supporting Mental and Emotional Well-Being
Student well-being is a growing concern for educators and parents alike. Academic pressure, performance expectations, and social challenges can take a toll on children’s mental health.
Creative activities offer a healthy outlet for emotional expression. Through art and creative exploration, students can:
- Release stress and anxiety
- Express feelings non-verbally
- Build emotional awareness
- Develop resilience and confidence
In 2026, classrooms that prioritise emotional well-being alongside academic success will create healthier learning environments.
Creativity Builds Focus and Patience
While creative activities are often associated with freedom, they also require structure, planning, and sustained attention. Activities such as painting, crafting, or project-based learning help students practise focus and patience naturally.
Through creative work, students learn to:
- Follow processes step by step
- Manage time and materials
- Complete tasks independently
- Take pride in effort, not just results
These skills directly support classroom discipline and academic learning.
Preparing Students for Collaboration and Communication
Modern education emphasises collaboration and communication. Creative activities often involve sharing ideas, working in groups, and presenting outcomes.
This helps students develop:
- Teamwork and cooperation
- Respect for different perspectives
- Clear communication skills
- Confidence in sharing ideas
Creative classrooms encourage participation and reduce fear of making mistakes.
Reducing Over-Reliance on Screens
Technology is an important educational tool, but excessive screen use can limit physical engagement and sensory learning. Creative activities provide balance by offering tactile, real-world experiences.
Hands-on creativity:
- Engages multiple senses
- Encourages movement and coordination
- Reduces screen fatigue
- Supports cognitive development
As digital learning increases, creative activities help maintain a healthy balance.
Creativity Encourages Lifelong Learning
When students enjoy the learning process, they are more likely to remain curious and motivated. Creative activities make learning enjoyable, personal, and meaningful.
Students who engage creatively tend to:
- Develop intrinsic motivation
- Explore interests beyond the syllabus
- View learning as a positive experience
This mindset is essential for lifelong learning beyond the classroom.
The Role of External Creative Programmes
While schools play a central role, enrichment programmes also contribute to creative development. Art-focused spaces such as Art Journey complement classroom learning by offering environments where creativity is explored without academic pressure.
These programmes reinforce the idea that creativity is not limited to art subjects but is a way of thinking applicable across all areas of life.
Rethinking Classrooms for 2026 and Beyond
The classrooms of 2026 must go beyond rote learning and standardised outcomes. Creativity is no longer an optional extra—it is a necessity for preparing students to navigate complexity, uncertainty, and change.
By integrating creative activities into daily learning, classrooms can:
- Support holistic development
- Improve engagement and well-being
- Foster future-ready skills
- Create confident, adaptable learners
Education in 2026 will not be defined solely by what students know, but by how they think, create, and adapt. Creative activities will play a central role in shaping that future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What age group are holiday workshops suitable for?
Most holiday workshops are designed for children aged 4 to 12 years, though some may cater to younger toddlers or older students depending on the programme.
Are holiday workshops purely educational?
No. Many workshops balance learning with fun, focusing on creativity, exploration, and personal development rather than academic outcomes alone.
How long do holiday workshops usually last?
March workshops are often 1–2 sessions, while June workshops may run over several days. December workshops range from single sessions to short programmes.
Are materials provided during workshops?
Yes, most workshops include all necessary materials. Parents typically only need to ensure children wear comfortable clothing.
Are creative workshops suitable for children with no prior experience?
Yes. Most creative workshops are beginner-friendly and designed to encourage exploration rather than technical mastery.
Can parents participate in holiday workshops?
Some December and weekend workshops are designed as parent-and-child sessions, allowing families to participate together.
How early should workshops be booked?
For June and December holidays, booking weeks in advance is recommended, as popular workshops fill up quickly.
Are holiday workshops good alternatives to tuition?
Holiday workshops complement tuition by developing creativity, confidence, and soft skills that traditional academic classes may not address.
What should children bring to a holiday workshop?
Most workshops provide materials. Comfortable clothing and a water bottle are usually sufficient.
Will holiday workshops continue to grow in popularity beyond 2026?
Yes. As parents seek balanced development and meaningful experiences, holiday workshops are expected to remain a key part of children’s holiday routines.